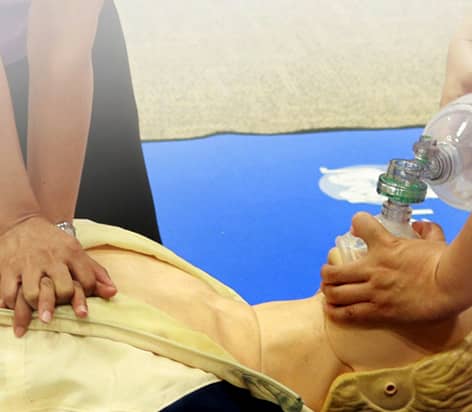
Advanced airway management is an airway management strategy that involves extensive skills, advanced training and equipment, and invasive procedures. Advanced airway management aims to develop a clear route between the lungs and the outside source of air, which could be the environment or a machine. Unlike jaw-thrust maneuvers or head tilt/chin lift in basic airway management, advanced airway management involves using advanced devices and state-of-the-art techniques.