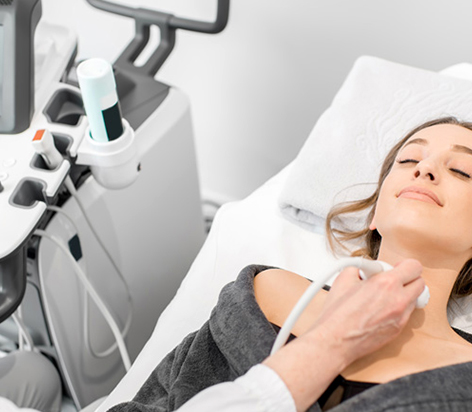
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland situated at the base of the neck that secretes thyroxine (T-4) and triiodothyronine (T-3) hormones. There are several thyroid gland disorders, ranging from a small, benign goiter to thyroid cancer. It is advisable to consult with a doctor if the patient experiences thyroid disorder symptoms. Usually, primary care physicians refer to expert endocrinologists if the patient is diagnosed with a thyroid disorder.