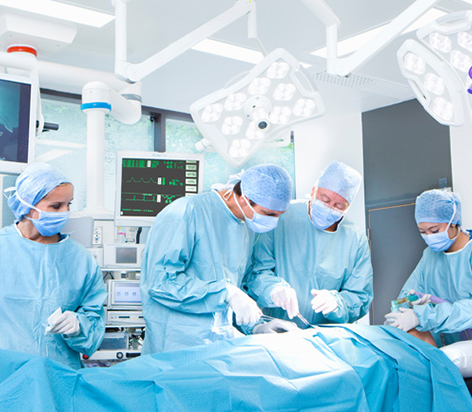
The surgery critical care unit comprises doctors trained in critical surgical care, experienced nurses, and advanced equipment to deliver the best healthcare facilities for diagnosing, supporting, and treating critically ill patients after surgery. The various surgical issues managed at the surgical critical care unit include hemodynamic instability, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, acute respiratory distress syndrome, abdominal sepsis, multiple organ dysfunction, acute renal failure, stress ulceration, candida infections, coagulopathy, post-operative infections, and complications related to anesthesia and sedation.