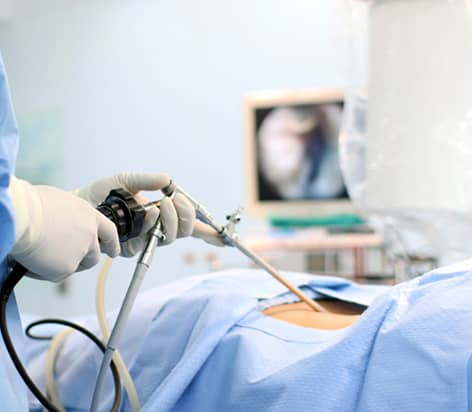
Laparoscopic surgery is performed with a laparoscope, a thin, long tube with a video camera at the end. It is inserted through a tiny hole to assist the surgeon during surgery. Basic laparoscopic procedures help remove the gallbladder, appendix, adhesions, and benign breast masses (lumps).